1. Benefits of Smart Cities
Smart cities offer numerous advantages that can improve the lives of their residents. The improvement of infrastructure is one of the most significant advantages. Technology is used in smart cities to monitor and manage infrastructure such as roads, transportation, and energy systems. This can result in improved maintenance, reduced congestion, and increased energy efficiency.
Another advantage of smart cities is improved public services. Data can be used by smart cities to improve public services such as healthcare, education, and public safety. Smart healthcare systems, for example, can remotely monitor patients, allowing doctors to provide better care. Smart education systems can use technology to provide students with personalised learning experiences. Data can be used by smart public safety systems to predict and prevent crimes.
Smart cities can also promote environmental sustainability. Technology can help smart cities reduce energy consumption, waste production, and carbon emissions. Smart buildings, for example, can use sensors to control temperature and lighting, reducing energy consumption. Data can be used by smart transportation systems to optimise routes, reducing traffic and emissions.
2. Smart Cities of the Future
1- NEOM Smart City, Saudi Arabia -
NEOM Smart City in Saudi Arabia is designed to be a sustainable and technologically advanced city, with a focus on renewable energy and innovation. It has the potential to attract foreign investment and talent, creating new job opportunities and economic growth for the region.
A. Features of NEOM Smart City, Saudi Arabia:
- Advanced technologies such as drones, robots, and artificial intelligence (AI) are being used for a variety of applications.
- With the use of renewable energy sources, you can focus on sustainability and environmental conservation.
- Transportation systems are being integrated with smart technologies to create more efficient and seamless travel experiences.
- Building a digital infrastructure to support smart city applications and services.
- Design and construction of a futuristic urban landscape using innovative designs and architecture.
B. Pros of NEOM Smart City, Saudi Arabia:
- Encourages economic growth and development by establishing new industries and job opportunities.
- Improves residents' quality of life by providing better access to healthcare, education, and other services.
- The use of smart technologies, it improves efficiency and convenience in daily life.
- Promotes environmental conservation and sustainability by utilising renewable energy sources and intelligent waste management systems.
C. Cons of NEOM Smart City, Saudi Arabia:
- The implementation of a large-scale smart city project necessitates significant investment and resources, which may put a strain on the budget.
- Some workers may lose their jobs as a result of the rapid development and adoption of advanced technologies.
- The implementation of smart technologies may also raise privacy and data security concerns.
- The development of a future urban landscape may result in the displacement and disruption of local communities and ecosystems. - NEOM is a Saudi Arabian futuristic city that aims to be the world's most sustainable and technologically advanced city.
2. Amaravati Smart City, India -
Amaravati is an Indian smart city that is intended to serve as a model for sustainable urban development.
A. Features of Amaravati Smart City, India:
- Intelligent transportation networks comprised of roads, flyovers, and highways.
- Sensors and automation are used in advanced water management systems to monitor and optimise water usage.
- Electricity and gas consumption smart metering and energy management systems.
- Waste segregation, recycling, and disposal facilities are all part of integrated waste management systems.
- Smart street lighting with automatic dimming and brightness control.
- Connectivity to high-speed broadband and free public Wi-Fi in designated areas.
- Online consultation, telemedicine, and e-health records are examples of smart healthcare services.
- Online citizen services, e-governance, and a centralised command centre for monitoring and controlling city operations are examples of digital governance services.
- Parks and green spaces with sustainable landscaping and water conservation features.
B. Pros of Amaravati Smart City, India:
- Improved quality of life for residents through the provision of better public services and amenities.
- Increased efficiency and productivity in city operations through the use of advanced technologies and automation.
- Enhanced economic growth and job creation through the development of a smart economy and innovation ecosystem.
- Reduced carbon footprint and environmental impact through the implementation of sustainable practices and green technologies.
- Improved the safety and security of citizens through the deployment of advanced surveillance and emergency response systems.
C. Cons of Amaravati Smart City, India:
- High initial investment costs for implementing and maintaining smart city infrastructure and services.
- Potential job losses in traditional sectors due to automation and digitization of city operations.
- Privacy concerns related to the collection and use of personal data by smart city systems and devices.
- Unequal access to smart city services and technologies among different socio-economic groups and communities.
- Dependence on technology and potential vulnerabilities to cyber threats and hacking attacks.
- Singapore Smart Nation - Singapore is well-known for its smart city initiatives and has a vision of becoming the world's first smart nation.
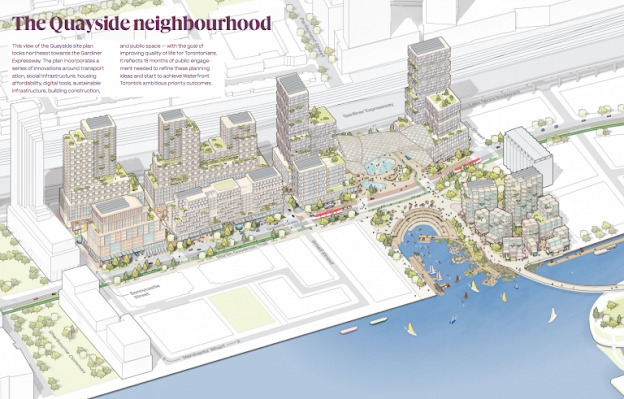
3. Toronto Waterfront Project, Canada -
The Toronto Waterfront Project aims to make the city's waterfront a smart and sustainable community.
A. Features of Toronto Waterfront Project, Canada:
- Smart waste management and environmental monitoring sensors.
- Public transportation systems that are integrated.
- Street lighting that is automated and linked.
- Intelligent traffic control systems.
- Wi-Fi hotspots in public places are available for free.
- Buildings that are both sustainable and energy efficient.
- Programs for community Engagement and social inclusion.
- Cultural events and public art installations.
B. Pros of Toronto Waterfront Project, Canada:
- Residents' and visitors' quality of life has improved.
- Increased economic growth and job creation.
- Environmental sustainability and carbon footprint reduction.
- Increased public security and safety.
- Public services that are more efficient and effective.
- Better public transportation and less traffic congestion.
- Increased digital connectivity and access to technology.
- Increased community involvement and participation.
C. Cons of Toronto Waterfront Project, Canada:
- High implementation and maintenance costs.
- Data collection and sharing may raise privacy and security concerns.
- The possibility of technical failures or malfunctions.
- Concerns about how smart city technologies will affect employment and job security.
- If access to technology and digital services is inequitable, marginalised communities may face social and economic exclusion.
4. Barcelona Smart City, Spain -
Barcelona is a forerunner in the development of smart cities, with ongoing initiatives such as smart transportation, energy efficiency, and citizen engagement.
A. Features of Barcelona Smart City:
- Efficient waste management through the use of underground waste containers and smart waste collection sensors.
- Intelligent lighting systems that adjust brightness levels in response to pedestrian and vehicular traffic.
- Digitalization of municipal services, such as the development of a single online platform for citizen interaction with city government.
- Data analytics and real-time monitoring are used to optimise energy consumption and lower carbon emissions.
- Smart water management systems are being implemented to monitor water quality and reduce waste.
B. Pros of Barcelona Smart City:
- Citizens' quality of life is improved as a result of efficient and sustainable city services.
- Carbon emissions and energy consumption are reduced, resulting in a more environmentally friendly city.
- Economic opportunities will be expanded as a result of the development of a digital ecosystem and the attraction of innovative businesses.
- Improved public safety through real-time monitoring and data analytics.
- Smart technologies have improved mobility and transportation.
C. Cons of Barcelona Smart City:
- Smart technologies and infrastructure have high implementation costs.
- Increased monitoring and data collection may result in a loss of privacy.
- Mistakes in technology and system errors cause disruptions in city services.
- Access to smart technologies and services is unequal, resulting in a digital divide.
- Dependence on technology, can lead to vulnerabilities in the event of a cyber attack or a technological failure.
- South Korea's Seoul Smart City - Seoul is a leading smart city, with a focus on using technology to create a more livable and sustainable urban environment.
5. Helsinki Smart City, Finland -
Helsinki aims to be a carbon-neutral city by 2035, with smart city initiatives such as smart mobility, sustainable buildings, and energy-efficient infrastructure.
A. Features of Helsinki Smart City, Finland:
- Intelligent transportation systems for traffic management, such as smart traffic lights and self-driving buses.
- To optimise waste collection, a smart waste management system with underground containers and sensors is used.
- Buildings that use renewable energy and have smart lighting systems.
- Citizens and businesses can use an open data platform to share and analyse city-data.
- A smart healthcare system that uses digital technology to improve patient care while lowering healthcare costs.
- Smart education system for students and teachers, with personalised learning paths and digital tools
- Sensors monitor water quality and detect leaks in a smart water management system.
- Wi-Fi City is a free public Wi-Fi network.
B. Pros of Helsinki Smart City, Finland:
- Citizens' quality of life will be improved as services become more efficient and sustainable.
- Increased economic growth via innovation and technology.
- Increased citizen engagement and decision-making participation through an open data platform.
- Environmental impact is reduced through energy-efficient and sustainable practises.
- Smart surveillance systems and emergency response systems provide increased safety and security.
- Better transportation with less traffic congestion and carbon emissions.
- Digital technology improves healthcare and education services.
C. Cons of Helsinki Smart City, Finland:
- High implementation and maintenance costs for smart city technologies.
- Data privacy and security concerns.
- The possibility of technical failures or malfunctions.
- If not all citizens have access to digital technology and smart city services, there is a risk of increased social inequality.
- Automation and AI technology may result in job displacement.
- Technology dependence may result in less human interaction and social isolation.
3. Challenges for Smart Cities
Despite the numerous advantages of smart cities, there are some issues that must be addressed. The high cost of implementing smart city technologies is one of the most significant challenges. Creating and deploying smart city solutions necessitates substantial investments in hardware, software, and infrastructure.
Another issue is the requirement for strong governance and coordination among various government agencies and departments. Smart cities necessitate close collaboration among various stakeholders, such as city planners, engineers, architects, IT professionals, and policymakers.
Furthermore, smart cities raise privacy, security, and data protection concerns. Smart city technologies generate massive amounts of data, and it is critical to ensure the security and privacy of this data.
4. Conclusion
Finally, the Smart Cities Mission is a large-scale project that aims to build 100 smart cities across India. Smart cities have the potential to improve citizens' lives, promote sustainability, and spur economic growth. However, the development of smart cities brings with it new challenges, such as high implementation costs, governance and coordination, and data privacy and security.
Overall, the Smart Cities Mission's progress is encouraging, and it is an important step towards a brighter future for India. By investing in smart cities, India can position itself as a global economic leader while also providing a more sustainable, efficient, and livable future for its citizens.


.jpg)